Sacm Is A Process That Supports Which Of The Following Stages Of The Service Lifecycle?
5 min. read
The service asset and configuration management process (SACM) is an of import process in the ITIL Service Transition stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. Online ITIL training gives detailed explanations on the part of SACM in the ITIL lifecycle. In this article, we will revisit the SACM process then we will discuss key knowledge which is also included in ITIL foundation exam questions past looking at the 5 process activities of the SACM process as a whole.

Revisiting SACM and its goals and objectives
Every service of an IT service provider is made up of components that contribute to the overall working of it. Let's say for a messaging service, individual components that contribute are servers, software, networks, admins who run the prove, and anything and everything else that chips in. SACM deals with these individual components, their attributes, and their relationships. Its omniscient presence through the service lifecycle makes it one of the almost of import processes in ITIL, and potentially the very first to be implemented.
Let's revisit the goals of the SACM process before nosotros focus on the 5 process activities. The first goal is to support the control objectives and the customer and business requirements. The second goal is to support an efficient and effective IT service management process. The third goal is to minimize the number of quality and compliance bug. And finally, the last goal is to optimize service assets, IT configuration, capabilities, and resources. The objectives of SACM is defining and controlling components of services and infrastructure. Information technology also aims to maintain authentic configuration information on historical, current and planned states of services and infrastructure.
Now that we have context, we can discuss the v process steps of SACM.
SACM: Management and Planning
The beginning activity is Management and Planning. It service providers accept several assets. Services, applications, tools, components etc. At that place must be a logical and structured versioning and release structure for configuration items in an Information technology service provider to eliminate defoliation. The methods for doing versioning, building releases, establishing configuration baselines etc. must be done in a controlled style. The methods for these activities are planned and documented in the SACM configuration direction plan.
Commencement, we need to plan on what we are going to consider a configuration detail. It might so happen that a particular visitor wants to label individual components of a server as a configuration detail. Some other visitor on the other side of the spectrum might determine to call a cluster of servers a configuration item. Each Information technology service provider must make up one's mind which level of labeling configuration items will piece of work best for them. A general practice beyond the service industry is to name a server as a CI, a router as a CI and sometimes, a monitor as a CI too. Individual components that make upwardly the CI are not managed individually and this must be taken into account.
SACM: Configuration Identification
The 2nd activity is of SACM is Configuration Identification. Afterwards creating the configuration direction plan, each configuration item of the Information technology service provider is named, labeled and the proper versioning of the configuration detail is washed. This will exist of tremendous help if the configuration items must be reviewed at a later stage. Proper identification of configuration items sounds like a small action, but it can be of immense value afterward in the SACM process. If the configuration items and their versions are non properly labeled it will be impossible to revert back to a configuration baseline land if a new version is deployed unsuccessfully.

SACM: Configuration Control
Then in the 3rd activity of SACM, Configuration Command, changes to the configuration items are managed and changes are washed in a controlled manner to each configuration item. At that place tin can be new requirements coming from the business for existing services, or a problem might be stock-still in an existing service. These all require changes to the configuration details to the configuration besides. For instance, each alter, version or release of the service must be updated as planned and described in configuration management program.
SACM: Condition accounting and reporting
The fourth activity of SACM is condition accounting and reporting. At this step, details and information nigh the configuration items are recorded and reported periodically. Reporting on the status of the SACM procedure activities will give the Information technology service provider a articulate view of how their service assets and configuration items are serving the objectives of the business. Likewise, the service provider tin discover which assets and configuration items should be kept as is, changed or removed from the definitive media library. The regularity at which status reports on SACM activities must be compiled and delivered should be agreed upon during service level negotiations. This will ensure that all stakeholders will take a firm view of the SACM process within agreed upon timelines.
SACM: Verification and audit
The fifth and the final activity of SACM is verification and audit. Afterwards updating a service or changing a configuration item of an IT service provider, there tin can be impacts on other parts of the service management. For case, afterward update on an existing service, if another service interacting with the updated service volition take an interaction or compliance problem, this will affect the service delivery to the customer. Therefore, upon updates, changes or implementations at an Information technology Service provider, verification, and auditing takes place to assure the updates have been implemented successfully and did not have whatever impact for other configuration items.
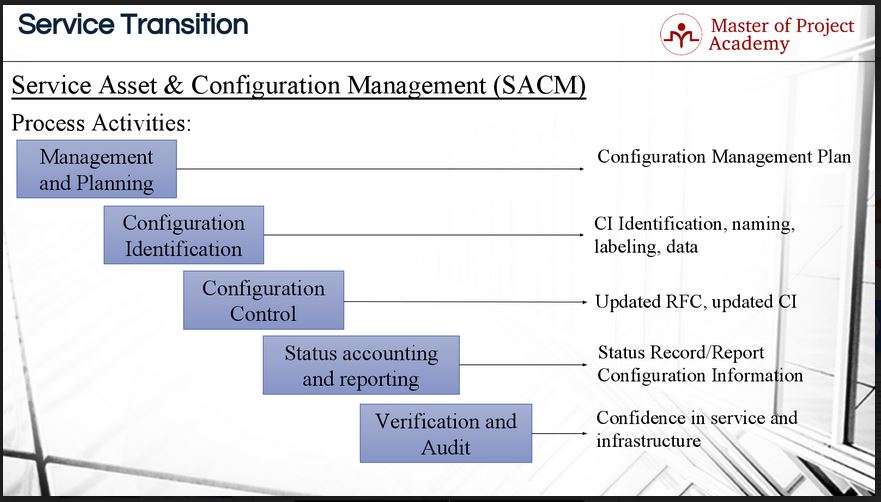
These v process activities support the service nugget and configuration management process. Without these five steps, the service asset and configuration management procedure cannot be successfully implemented. An IT service provider needs to have knowledge of all the configuration items that forms part of the IT infrastructure and these configuration items must be clearly identified and labeled. Any changes to these configuration items must be strictly controlled to ensure that no service disruptions accept place. The status of the service avails and configuration items must be reported on regularly to all stakeholders. Regular reports volition help to highlight any problems of improvements that need to be done. The concluding step, verification, and auditing is a crucial step to check whether all updates take been successfully deployed and that no other assets or configuration items accept been affected downstream.

SACM
Review by: Corey Allen
5 / 5 stars
Source: https://blog.masterofproject.com/sacm-process-activities/
Posted by: howejuserebeaven.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Sacm Is A Process That Supports Which Of The Following Stages Of The Service Lifecycle?"
Post a Comment